Three spinal mobilisations you can do daily without a therapist
Your FREE 10 minute posture meditation
In the client's own words...
What is the essence of Precision Movement? (KT on film!)
Wearables - say What-ables?
Can you believe it? Technology has now reached posture! Technology now called "wearables" have become accessible to the public. Consisting of a wearable piece that is linked to an app on your phone it tracks how you sit and stand and transmits a gentle vibration to remind you to sit up straight when you start slouching. In this article I reveal the most popular wearables for 2016, the upside and the downside of using them and I explain why adopting one position for long periods of time is detrimental to the health and wellness of your body. Read on to find out more...
The wearables of 2016
Lumolift is a small sensor that you place on your t-shirt at chest level. It measures the angle of your torso and gently vibrates to remind you to sit up straight if you start slouching.
ALEX is a wearable neck device that sits around the back of the neck monitoring alignment and sending out a vibration reminder when the wearer begins to slouch. It is currently crowdfunding through Kickstarter so not available to the public right now.
The upside
I am all for new technology. Technology is woven into every part of our life now so it is natural that designers and product developers are thinking up ways to influence health, wellness and now posture.
I think a positive about wearables is that they provide some sort of consistent reminder of what an individual is trying to achieve - in this case better posture. When trying to improve posture in sitting, standing and corresponding movement, consistency is absolutely imperative to create change. We build programmes for movement and posture that are stored in our brain. The more we use these patterns the stronger they become. I liken it to drawing a line in the mud with a stick - the more times you do this the deeper the groove in the mud becomes. When we work on posture or a new movement pattern we cannot overwrite an old programme in the brain we can only build a new one and try to make it the preferred one. The key to making a movement or posture pattern dominant is to repeatedly use it so it becomes stronger. In essence a wearable can act as a consistent reminder to make a preferred posture pattern stronger.
The downside
As a posture and movement specialist sitting and standing better is not just a matter of sitting/standing "up". The changes in posture that an individual needs to make are as individual as their injuries and or discomfort.
Everyone I work with here at Precision Movement receives bespoke programmes and bespoke cues for improving and changing posture. What is really key in sitting and standing posture is the information you give an individual to elicit change.
Often if you tell someone to sit up straight or stand better they get taller but often lean back. They hinge from the mid-back and the position of the shoulders and head stay the same in relation to the chest and back. This is no more correct than slouching forwards and can lead to as many if not more problems in time. It is also common for an individual to "hold" themselves in a better posture creating a higher resting tension in muscles which is both metabolically inefficient and will lead to muscles becoming overworked, tired and sore.
Posture and movement are intricate, delicate, and sensitive systems that require subtle, measured changes to achieve optimal joint centration and muscle balance.
I give my clients a 10 minute audio posture meditation to listen to on their commute to work, during their lunch break or on their commute home to remind them of the cues for better posture. You can listen to it below or click here to the article I wrote about it.
Posture isn't static
The body is built for movement. It is well known and certainly well written about that sitting at a desk is not good for posture. It is true that sitting creates undesirable postures but stagnancy is equally to blame for poor posture, discomfort and injury.
Movement helps prevent muscles, joints and connective tissue from stiffening up. Movement helps pump blood into muscles, it pushes lymphatic fluid out and both provide cells with nutrients and remove toxins. This also helps reduce discomfort.
Rather than trying to sustain one good posture all day it is also beneficial to stand up and walk around the office or go out for lunch. At Precision Movement we often give individuals stretches and mobilisations to do in their chair just to create a bit of movement away from sitting still for long periods.
The solution
I think wearables could have a place in reminding an individual on a consistent basis to think about a better way to carry themselves. But (and I rarely ever use the word but), the information given to an individual about how to improve alignment is absolutely crucial to the success of improved posture.
So in conclusion, the cues that an individual is given to improve posture are the real gold here, the wearable can act as a positive reminder in the early stages of change. I would recommend anyone wanting to use one to work with a posture specialist and incorporate the wearable in sessions. I would also recommend a programme of stretches and mobilisations that can be done in an office setting also to encourage movement. The ultimate goal is to find good posture and movement without the use of external stimulus so an appropriate phase out of the wearable should be considered also.
How corrective exercise differs from regular exercise
The number one question I get asked is "Are you a physio?" - unfortunately I cannot lay claim to this esteemed profession! I am not a physio. The second question is, "So are you a personal trainer then?". Again I cannot say I am a Personal Trainer either - well not anymore. I fall somewhere between the two and work under the grandiose title of "Corrective Exercise Specialist". This line of conversation invariably leads to a discussion about what type of exercise I do and how it differs from gym training. I will now humbly attempt to explain in an effort to give you a better understanding of the difference.... Wish me luck!
What is corrective exercise?
Corrective exercise is a special type of exercise usually used as part of the rehabilitation process in healing and recovery from chronic pain, injury or surgery, or given to those who suffer from poor posture. The emphasis really is on optimal alignment, stability, mobilisation and then strength development.
In comparison regular exercise that you might do in the gym or in sports has a different goal - often increased fitness, body shape change, weight loss etc. As the goals are different the exercises and movement given are bigger and incorporate more muscles. This helps co-ordination for sports and is also effective for conditioning the body to change shape and increase fitness. If I were to give these exercises to someone who is in pain and has poor alignment, poor stability, mobility and strength they would not be able to perform them effectively and could potentially hurt themselves further.
It's important to mention here that corrective exercise also forms a foundation for all movement and exercise. If your foundational principles are good then your risk of injury is much reduced. When clients come to Precision Movement with fitness goals we still take them through foundational principles to make sure alignment, stability, and mobility is optimal for more complex movements.
The types of exercises
The majority of exercises I do with clients at the beginning of their programmes are floor or swiss ball based. I ask them to repeat the repetitions many times to elicit postural change and I also ask them to engage in mindful exercise which includes some psychology techniques. Corrective exercise rarely makes you sweat and definitely doesn't increase your heart or breathing rate. It is not easy though! The areas we stretch are usually tight and stiff and the muscles we train are weak to begin with. When clients adapt and improve, programmes are updated to challenge them further.
A classic exercise I teach clients is the horsestance series. It looks very easy but it is actually quite challenging. Before clients can do this exercise effectively I'll also teach and often reset their breathing mechanics, help them effectively activate their core and how to activate stability through their hands and feet. When the exercise is performed correctly it is exceptionally effective in training stability and forms a solid foundation for more complex movements that you would do in the gym or in sports.
Typical exercises you might see in the gym are squats, lunges, pullups and pushups. These are all neurologically complex movements meaning the brain needs to send a huge amount of information to the muscular system to perform the movement successfully. You might use a kettlebell swing which is a dynamic form of a deadlift pattern. Running, martial arts and many other sports are also exceptionally challenging to the body and brain. To perform these exercises and sports well you'll need optimal joint stability, understanding of core function, breathing mechanics, optimal joint mobility and to minimise the risk of injury good alignment throughout the body as well as in the movement.
When does corrective exercise become regular exercise?
At Precision Movement we are specialists in change. Our goal with everyone is to get them to a fully functional movement state for life and whatever sports they participate in.
We don't want someone lying on the floor doing a mundane exercise forever. We may ask someone to do this in an early stage of rehabilitation to get certain muscles firing but when they adapt to the exercise we make it more challenging. All the exercises we give have many many progressions right up to regular exercise that you'll recognise well. Perhaps the difference in giving regular exercise at Precision Movement is we might make changes or modifications that are specific to an individuals needs eg. A static lunge might include a band to emphasise the inclusion of the hip stabilisers that have a tendency to be lazy - they might now be strong but the band acts as a reminder for the individual to maintain good knee alignment.
In a way, we use corrective exercise like servicing a machine. A machine that has been running for a while might need some parts changed, an oil or water change. Similarly, we'll do a maintenance check and make sure all the stabilisers are firing correctly and alignment and mobility are good.
For more information on corrective exercise for postural alignment, pain relief and management of injuries and degenerative conditions please contact us.
The back bone of life
Last week I was asked to speak at the L Club in on Sloane Street about the importance of the spine for health throughout life. I thought I would share with you what I shared with the audience of the L Club how your spine develops, what injuries it is most vulnerable to at certain parts during your life and how you can minimise the risk of injury as you age. If you are tempted to just read what it says under your current age bracket this would be foolish. Remember what you have done in the past and what you do now will all influence how the spine will respond in later years. Read on to find out more....
0-3 years
When we are born our spines are curved like a shell. In the first 2 years up to when we walk we go through huge amounts of development and change in the spine. We learn how to move it and stabilise it and to sit up, crawl and walk the spine changes alignment. As we grow our spines take on three curves - cervical, thoracic and lumbar and these curves are responsible for maintaining good posture, keeping our intervertebral discs in place and providing shock absorption. This is one of the most important developmental stages of our lives and we should never underestimate the value of babies learning to move efficiently and effectively. The movements and postures that babies learn here serve them for the rest of their lives which means if faulty movements are developed it will affect movement, co-ordination, posture and strength development in later years.
3-21 years
This is the time when we should move and learn sports. Jumping around and pounding on our bones is the best way to make them dense and strong coupled with a good intake of calcium from leafy greens and vitamin D from the sun as well as good overall nutrition. Any weight bearing sports are good for bone density development (swimming is a non-weight bearing sport). Intense learning of sports is not recommended until age 7. Ideally children should try out lots of different activities. At age 7 if children show an interest in a particular sport they have enough neural development to learn more intensely. Children should not lift heavy weights as it can stunt growth.
21-30 years
When we get to 21 we have fully grown but we can still increase our bone density. Bone density is exceptionally important for the prevention of osteoporosis. Between 30-35 our bones begin ageing and it is no longer possible to increase our bone density - we can only slow the rate of decline. This is effectively done by weight bearing exercise such as strength training. The discs between your vertebrae have fluid and a jelly like substance inside which acts as part of the shock absorption I mentioned earlier. At at 30 our bones cannot get any denser. From here our bones go through a process of becoming less dense.
30-45 years
This is the time when the spine is most vulnerable to disc injuries. Mostly because of our lifestyles - too much sitting and not enough movement. Up to age 45 the discs are refilled with fluid each night as part of the recovery process when we sleep. This is why you are taller in the morning and shorter at night! One of the reasons why disc injuries happen between 30-45 years is because of years of 'ligamentous creep' the connective tissues in the spine stretching over time to accommodate poor posture. Ligaments are the strongest structures in our bodies connecting bone to bone and they give our skeleton stability. Once ligaments are stretched they do not go back to their original length. Over time, years of time, it makes the spine unstable and then the discs become vulnerable to pressing out on to the nerves.
45-55 years
Past 45 the discs begin to dry up and the spine becomes stiffer. This actually has an advantage as the discs are less prone to pushing out against the nerves because they are less plump. However, less fluid in the discs means loss of disc height. Firstly, you lose height which is not so bad. Secondly, your vertebrae are much closer together so the ligaments become lax and can create instability. This hinders movement, particularly rotation, and can also lead to bone spurs and stenosis.
55 onwards
Depending on what you have done or not done with your body you may experience some pain or injury in your spine as you age - common but not normal issues are osteoporosis, arthritis, spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis and postural imbalance. What I always find interesting is that most people as they age will have some sort of disc degeneration but not all suffer with pain from it. The key here is movement - the more active you are the less likely you are to feel pain.
The most important point here is what you can do to minimise the risk of injuries and diseases when you are older. Once you have these issues they can be managed but they are not reversible.
If you want to know more about minimising the risk of spinal complications when you are older or maybe you have a spinal injury that you'd like to know how to manage better then contact me at
.
5 common desk bound injuries and how to avoid them
The office environment does not lend itself to an optimal pain free and posturally aligned existence. Our postural alignment is often the last thing we think about until we begin to experience pain. Here are the 5 most common aches and injuries from a desk bound environment and how to avoid them.
RSI - Repetitive Strain Injuries
This is an umbrella term given to a collection of upper limb injuries including thoracic outlet syndrome, double crush syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, golfers elbow, tennis elbow..... These injuries mostly start in the neck and shoulder area and commonly come from postural misalignment.
How to avoid it
Try to avoid typing for long periods of time - take a break for a few minutes every half hour or so. If you have a smart phone with voice activation then use it to give your hands, fingers and wrists a break. Take time off your phone and tablet by reading a newspaper or a book or listening to music.
Low back pain
This is probably the most common complaint of all desk bound workers. Back pain can occur for many different reasons and your office environment can contribute and exacerbate it. The most common cause of back pain is slouching in your chair and then sustaining postures for long periods that encourage certain structures to be stressed more than others.
How it avoid it
Sitting for long periods is not great for your back. Make sure you move frequently throughout the day. Get out of the office for lunch, walk to the water cooler, take a few flights of stairs up or down between floors, get out a tube station early and walk the remaining distance to your office. If you can exercise before or after work or even during your lunch break. Without fail get your workspace assessed by an ergonomics specialist - insist on one from your company.
Upper mid back pain
Another common compliant especially from writers, architects, artists and anyone who hunches over their desk. Mid thoracic aches and pains often come from an imbalance between the muscles in the front of the shoulder and chest area being too tight and the upper back muscles being too weak. A common occurrence is a strained feeling which comes from the back muscles being stretched but at the same time contracting to stop you from collapsing over your desk. It is call tautness - the muscles are weak and tight at the same time from being over worked.
How to avoid it
Work on your upper back alignment - do not hunch over your desk. If you are writing and reading or drawing a lot then invest in an architects desk that you can tilt to an appropriate angle for your work. Invest in a few sessions with someone who can teach you upper back exercises and stretches for postural alignment that you can do daily to strengthen your upper back.
Neck pain
Neck pain is exceptionally common especially these days with the use of smart phones and tablets that we look down to use. Even at your desk you are inclined to crane your head forwards towards the computer screen in front of you. This puts incredible strain on the neck and can cause injuries such as a cervical disc prolapse.
How to avoid it
Mobilise your neck throughout the day with head rolls and shoulder rolls. If you have a chair with a head support consciously press your head back into the support whilst you work. Make sure your chair alignment is assessed by an ergonomics specialist. This will help correct the alignment of your head and neck as you work. Do not place the phone between your ear and your head - use your loud speaker or invest in a head set. Use a stand for your tablet if you are working at your desk to avoid hunching over it.
Shoulder pain
Shoulder pain can come from excessive use of smart phones and even typing on your keyboard. Mostly pain will come from misalignment and if often associated with neck and mid thoracic issues. Shoulders are vulnerable joints so seek out help with postural alignment.
How to avoid it
Mobilise your neck throughout the day with head rolls and shoulder rolls. Make sure your workspace is optimally aligned for your arms and shoulders. Take a rest from your smart phone - some phones now have voice activation so you can give your hands and arms a rest from the constant furious typing. Find a corrective exercise specialist or a rehab specialist to help you with your shoulder alignment.
General advice
If your pain does not resolve itself within 7-10 days and if it gets continually worse then seek treatment from a physiotherapist or osteopath. Early treatment often results in a quick recovery. It is tempting to ignore aches and pains until they become unbearable - the longer you leave something the longer it will take to recover. If you would like more information on how to resolve a desk bound injury please email me at
KT@precisionmovement.co.uk
.
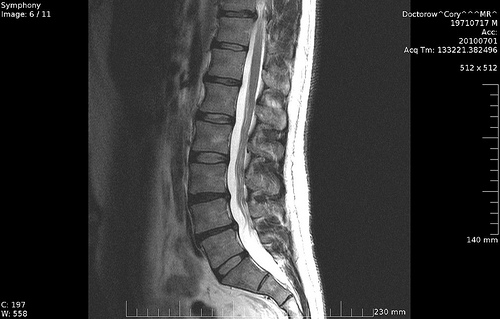
Looking inside the body for the cause of your pain
Scans help identify whether structural damage is causing or exacerbating pain. Personally I think knowing is better than not knowing so I would always go for a scan. But what scan is best for you? And what are the pros and cons to scans? Read on to find out more....
What scans do
A scan can show nothing even though you may be experiencing excruciating pain but it can rule out structural damage so you can begin looking at other factors. If a scan does show evidence of what is causing your pain this can provide a sense of relief. It also helps the specialists, therapists and rehab practitioners tailor your recovery plan more effectively. The important thing to remember is that whatever the scan shows, it is just information. It is the decisions and actions you take from learning this information that will form your recovery plan. The most common scans used for back pain are x-rays and MRIs.
X-rays
An x-ray can tell you if there is anything wrong with your bones. An x-ray will show up breaks, fractures, bony change like arthritis or bone growths called spurs. What is can be really useful for in terms of potential causes of back pain is showing loss of disc height. Structural damage to discs and also ageing can cause the discs to reduce in height. This results in your vertebrae (bones that make up the spine) sitting closer together. If the cause of reduced disc height is not known it may be better to opt for an MRI to gain a more comprehensive picture of what is going on.
Pros: cost effective, reduced wait time for scan if any
Cons: restricted information, small dose of radiation
MRI scans
An MRI scan (magnetic resonance imaging) can show you bones, muscles, connective tissue, nerves, discs, arteries and all other structures in the body. It takes a series of images at very small slice increments and then puts it all together to create a complete picture. Often with an MRI scan you get several slices to view which enables consultants to 'look through' structures beyond the surface. It gives you a comprehensive view of everything in the area of pain.
Pros: more accurate diagnostic tool
Cons: Expensive, often wait list on the NHS but can go private, closed MRI scanners can be claustrophobic to some so ask for an open top one if available.
Getting an MRI quickly
There is often a wait list for an MRI scan on the NHS. You can get a scan quickly through private medical insurance but if this is not an option there is an alternative solution. Vista Diagnostics offer MRI scans from £200 with short notice appointments available. You could potentially get a scan within a day and results within 2 days of your scan. For more information visit www.vistadiagnostics.co.uk. This option could eliminate much anxiety and frustration which can make your condition worse. It could also mean starting treatment earlier so you can get better faster.
Results
Whatever can you have make sure you understand the results. The radiologist who interprets the results of your scan will send you and your specialist a letter explaining what has been found. Once you know if there is any structural damage you can make a more informed decision about how to proceed with treatment. If nothing is found that is totally ok - there are many people who suffer with back pain who do not have any structural damage. Often pain is caused by poor posture, your lifestyle habits, your nutrition choices. Discuss treatment options with your specialist and ask about manual therapy and corrective exercise as well as alternative forms of pain relief like acupuncture.
Key points
The key points to take from this are firstly MRI scans are the more comprehensive scan option and secondly, whatever the scan shows it is just information that will help you make a better decision about your recovery plan. If you have structural damage like a disc prolapse or stenosis it's ok - you are not going to die! Many many people have structural damage. The most important thing is to put a multi-disciplinary recovery and management plan in place. For more information on back pain and injury recovery and rehabilitation please contact me at KT@precisionmovement.co.uk.
What exercises can I do for back pain?
I love this question! It is something I get asked when I am out socially and people discover I work with back pain and injuries. The truth is no one set of exercises fits all back pain problems. In fact, every person I see in my practice is so completely different it never ceases to amaze me. For instance someone with a disc prolapse may really benefit from a back extension mobilization and stretch. If I give the same stretch to someone with stenosis (bone spurs) it will push on the already smaller spaces where the nerves exit the spine and aggravate their condition. It gets more complex when I have someone who has both of these conditions or multiple spine issues. Believe me there is no one size fits all. Here are some golden rules about exercise that apply to most all back pain sufferers.....
1. MOVE!!!
If there is one thing you take away from this article please make it the importance of movement. Every day moving around trumps sitting or lying still every time. The key to movement for relief of pain, especially when it is very sore, is to do it gently. If you are desk bound at work get up and walk around, take the stairs for a few floors, get out for lunch, walk to the water cooler. Walking can often provide a sense of relief (however if it makes it worse and sitting relieves it then take a rest periodically). Things to avoid are heavy lifting and too much bending over to pick things up off the floor.
2. Specific back mobilizations
I recommend my clients do gentle back specific mobilizations upon waking daily to ease the back into the day. If you suffer from stiffness upon waking these mobilizations can be very effective at reducing your pain in less time. Ideally you should have someone show you how to do mobilizations that are specific to your back problem. However, you can download your copy of the
Precision Movement Daily Mobilizations
that I give my clients
. Be sure to read the instructions carefully - small and gentle is key!
3. Corrective exercise for postural alignment and stability
Here lies the key to getting your back pain sorted. Corrective exercise focusses on your alignment, stability and core activation and moves your through stages of development from small isolating exercises right up to functional often loaded movement. This is where you can get mobilizations, stretches and exercise tailored to your specific condition. At Precision Movement I always give programmes for the relief of pain when your back is sore, daily home programmes, a set of stretches to do at your desk, and a programme for the gym as required.
4. The Gym
If you are suffering from intense back pain avoid lifting heavy weights. Weights create axial (vertical downward) loading on your spine and if you are already in discomfort the worst thing you can do is increase the pressure on areas of discomfort. You could seriously hurt yourself. Do not use machines as a substitute either. Machines isolate and stress your big muscles without using the stabilizers around the joints. If your back is sore the last thing you want to do is make it more unstable or have the larger muscles pulling on it. It would be better to do some gentle yoga or pilates work being mindful of your postural alignment and core activation until your back settles. If you are a regular gym user make sure you have a professional with rehabilitation experience look over what you are doing.
5. Running, biking, rowing and cross trainer cardio machines
If you would like to do some cardio work the key to not aggravating your back is to change it up. Sustained positions can be aggravating for the back. When your back is sore avoid jumping and running as a greater amount of load is placed through the spine and this can be jarring to the back. Cycling and cross trainer are gentler options for cardio and can be alternated. For the bike make sure you are sitting properly and have a professional check your position before you begin. I would avoid rowing when your back is bad especially if you have any disc prolapses and proceed with caution under supervision.
For more information about how corrective exercise can help your specific back pain or injury contact KT at
. Download my eBook '7 steps to getting your back pain sorted' - the link is on the right hand side (just scroll up a bit!).
My top 5 reads for chronic back pain sufferers
I love sharing knowledge! Which is why I have compiled a list of my top 5 reads for chronic back pain sufferers. They are all easy to read and most of them have tips and information you can apply immediately. If you are suffering from chronic back pain and you really want to know what to do about it and how to handle it then read on....
1. Explain Pain by David S Butler and Lorimer Moseley
A comprehensive information packed book that explains how pain comes about and what it means. Although it's a little pricey I think it is must read for chronic pain sufferers.
2. Painful Yarns by Lorimer Moseley
A wonderfully entertaining book that uses the authors personal anecdotes to explain the mechanisms of pain and about taking responsibility for recovery.
3. Treat your own back by Robin Mackenzie
This is a good book for anyone with disc prolapse. It gives easy to understand advice and information and is a great starting point for approaching recovery.
4. Sitting on the job by Scott L Donkin
This book is a bible of information if you are a desk bound office worker with back pain or any workplace associated injuries such as carpal tunnel or RSI.
5. How to eat, move and be Healthy by Paul Chek
I recommend this book to everyone I meet. It looks at all areas of your health and wellness and is an integral part of healing nad recovery from any pain or injury.
5 top must-have tips for a long healthy career
If you are in business and or climbing the corporate ladder you'll know all too well that feeling of invincibility. It's a divine trait and can also be equally as detrimental - unsuspectingly to your spine and your heart.
Clients come to me in their mid-30s to mid-40s with back, neck and shoulder pain and in their mid forties to fifties with heart trouble. One way or another, a life time of stress will get you. And when it does you will have to stop completely to heal and recover. There is nothing more soul destroying than being close to the height of your career and having to take 6 months or longer off because you can't get out of bed. It's probably not something you think about at all - and I am with you that you shouldn't have to. An awareness and application of a few basic support systems can minimise the risk of present or future work related back pain and injury. Here are my top 5 counteractions to minimise the risk of irreparable damage to your spine so you don't have to think about it!
1. Your state of mind. No one is invincible. If you are striving to achieve a top job it is an endurance race not a sprint. Pace yourself and take time out. The first step is to rethink the invincibility cloak - save it for dress up with the kids!
2. Your body heals and recovers from the stress you put it through daily when you sleep. Sleep is not an option for minimising injury and illness prevention in the future - it is a necessity. Both quality and quantity are important. Aim to sleep for 8 hours a night ideally between 10pm and 6am. Take out any electronics from your bedroom and switch off lights at the mains. Your room should be pitch black and as quiet as possible for a really good quality of sleep.
3. The food you put in your body becomes you. If you eat sugary processed foods your body will be starved of the nutrients that heal and restore from daily stressors. Also not eating enough will cause stress and impair effective recovery. Every cell in your body is renewed over 7 years. So short term fixes will not work well for injury and illness prevention in the future. Make a commitment to yourself to make a change for life - feed your success by eating what nature grows for you.
4. Movement is absolutely essential for injury prevention. If you sit at a desk during your working day you MUST make an effort to move either in the morning or in the evening. Exercise plays a direct role in maintaining good posture and keeping your joints strong and stable. A balance of high intensity and restorative exercise is also important. Too much high intensity will stress you out and could lead to an over-training injury. The quality of movement has a huge impact on how successful it becomes for injury prevention. If you turn up the gym and have a go on what looks good or manageable I would suggest seeking advice. At the very least find a good trainer or corrective exercise specialist with experience, top qualifications and a passion for their job to design and regularly upgrade a programme for you.
5. Strive for a balanced life. Spread your energy and interests wide. This idea is about giving your brain a new stimulus - a chance to work in another way. It is said that a change is as good as a rest right? So change your stimulus to give your brain a rest. Mental stress is as detrimental to your body as physical. This will mean stepping away from the office - and the blackberry.
Implementing and making a habit of these 5 suggestions helps to optimise your health to give you the best possible opportunity to enjoy a long, healthy and successful career.